10/18
Band gap: determined by the electronic states and atomic configurations of semiconductors, it reflects the energy required for the valence electrons of the atoms that make up this material to be excited from a bound state to a free state; the band gap is an important characteristic parameter of semiconductors. A band gap of zero indicates a metal, a large band gap (generally greater than 4.5 eV) indicates an insulator, and a medium band gap indicates a semiconductor.
10/18
The conduction mechanism of semiconductor materials is achieved through two types of charge carriers: electrons and holes, which are classified as N-type and P-type. Diamond, as a group IV element, can be viewed as having a crystal structure formed by two face-centered cubic structures translated along the body diagonal by 1/4 of the lattice constant. Carbon atoms bond with four neighboring carbon atoms through covalent bonds using sp3 hybrid orbitals, forming a tetrahedral structure. By doping diamond with appropriate elements, its electrical properties can be altered, allowing it to be widely used as a semiconductor material in electrical devices.
10/18
Research shows that diamond, as a member of the ultra-wide bandgap semiconductor materials (bandgap width 5.5 eV), possesses a range of excellent physical and chemical properties, such as high carrier mobility, high thermal conductivity, high breakdown electric field, high carrier saturation velocity, and low dielectric constant. This has garnered significant attention in the high-tech field, especially in electronics, and it is recognized as a promising new semiconductor material. Based on these advantages, it helps to reduce the mass, volume, and lifecycle costs of electronic components, while allowing devices to operate at higher temperatures, voltages, and frequencies, thus enabling electronic devices to use less energy while achieving higher performance.
10/18
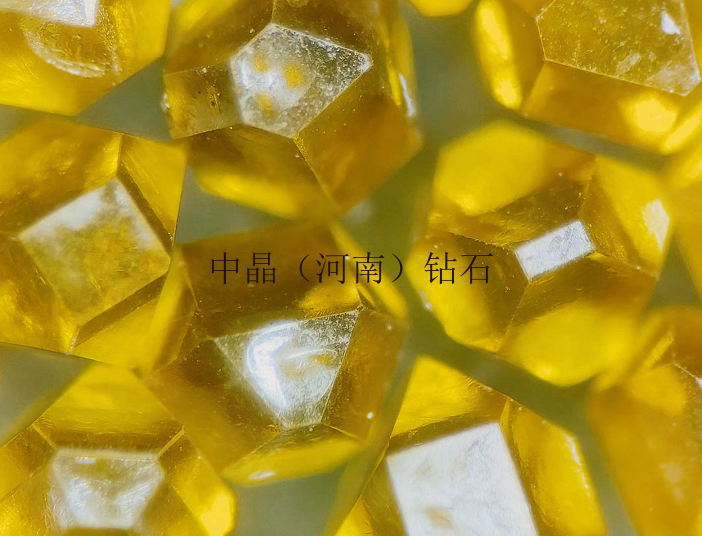
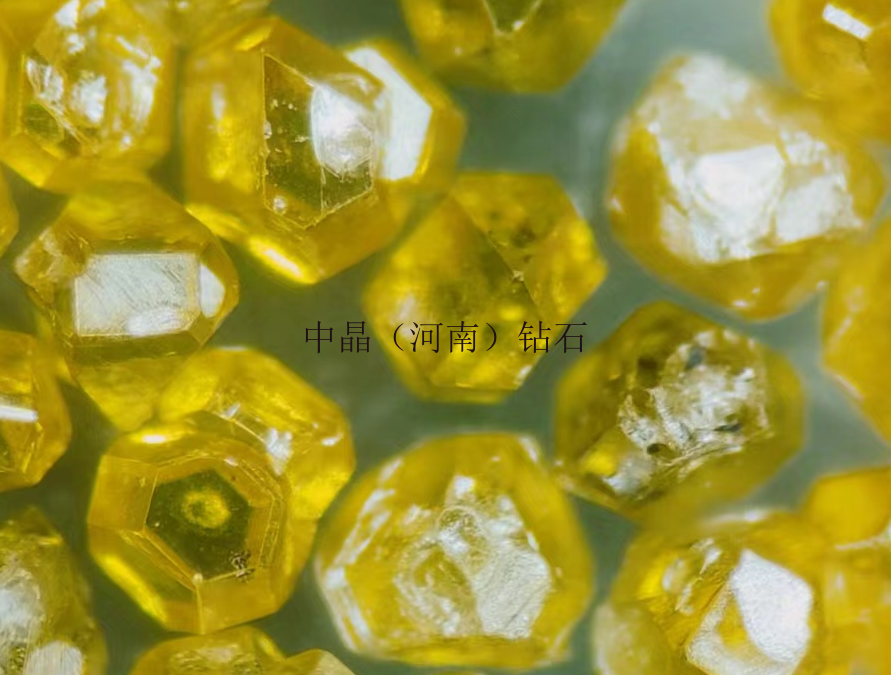
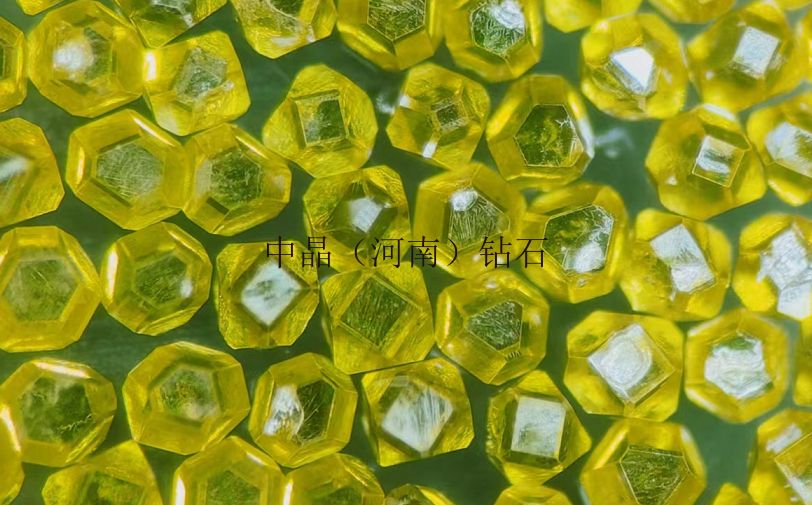
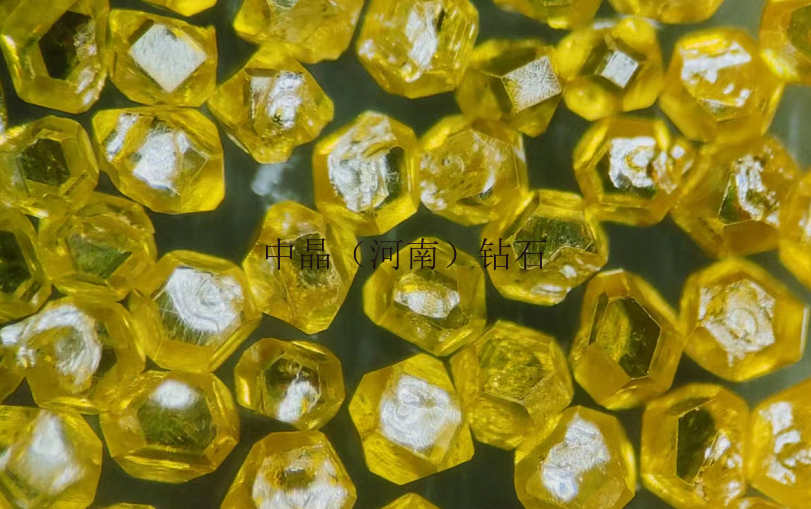
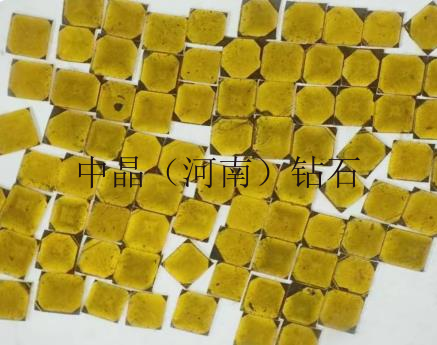
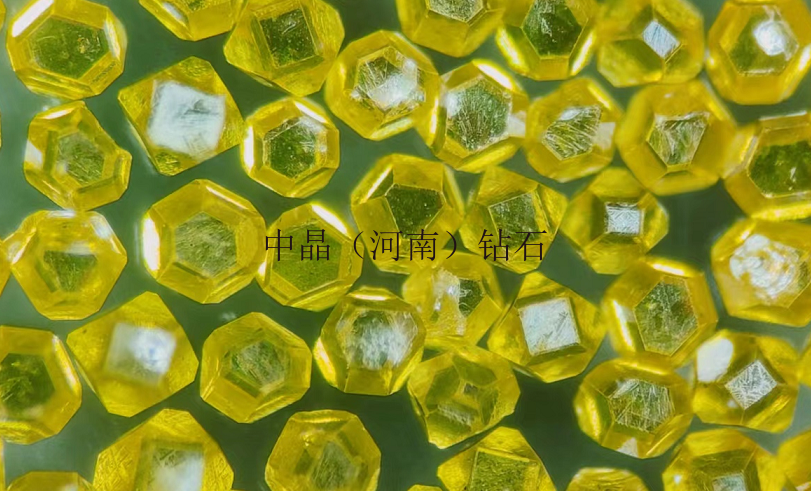
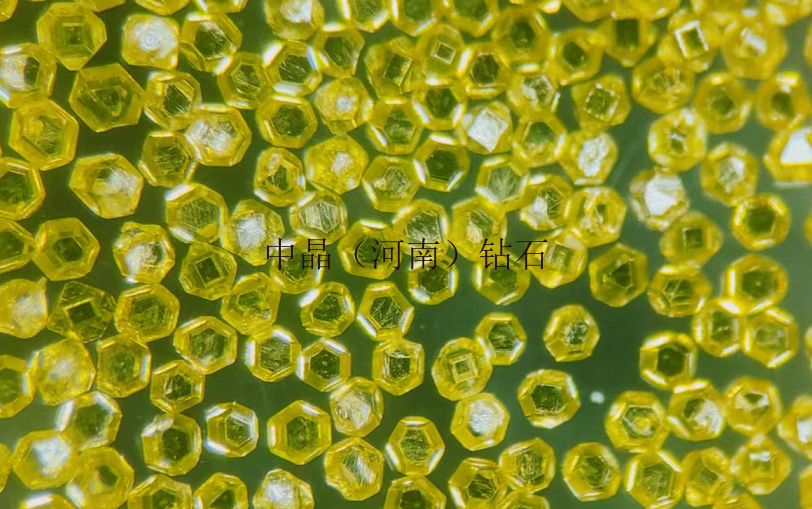
Diamond micro-powder refers to diamond particles with a particle size finer than 54 microns, with a chemical composition of carbon, and is the hardest material in nature. Diamond micro-powder is formed from diamond single crystals through processes such as crushing and ball milling, resulting in micron or sub-micron level ultra-fine diamond powder. Diamonds have high strength, good wear resistance, a Mohs hardness of 10, and a microhardness of 10000 kg/mm², which is 1000 times higher than quartz and 150 times higher than corundum. Therefore, diamond micro-powder, as an ultra-hard abrasive, possesses unparalleled grinding capabilities compared to other products and is increasingly valued by industrially developed countries.
10/18
The stability of upstream supply combined with the huge demand from downstream industries has led to rapid growth in the diamond micro-powder industry. It is expected that by 2025, the output value of diamond micro-powder in China will reach 2.61 billion yuan, with a CAGR of 10.6% from 2020 to 2025. In the future, with the stable development of upstream and downstream industries and support from national policies, the prosperity of the diamond micro-powder industry is expected to continue to improve.
10/18
The "14th Five-Year Plan" has established the broader context for the transformation and upgrading of China's manufacturing industry. Representative industries in this transformation and upgrading, such as photovoltaics, chemicals, machinery, and aerospace, have raised high requirements for materials and processing tools. Diamond micropowder has excellent performance and good chemical stability, and its advantages are further highlighted in the upgrading of the manufacturing industry. The transformation and upgrading of the domestic manufacturing industry not only create a favorable macro environment for enterprises in the diamond industry chain but also directly stimulate the demand for diamond-related products, providing strong growth momentum for the diamond industry.
10/18
CBN and diamond are classified as super abrasives. The reason they are called super abrasives is that the hardness of these two abrasives is far greater than that of other traditional abrasives. So, how can we distinguish between the two super abrasives, and how should we choose the right abrasive for our own grinding wheels? First, we need to understand the characteristics of both.
10/18
Glass cutting discs have a strong holding ability and high wear resistance due to the binder's effect on diamond abrasives, making them particularly suitable for the precise cutting and grooving of optical and electronic components. Resin cutting discs use resin as a binder and fiberglass mesh as a skeleton, combining various materials, and are especially effective for cutting difficult materials such as alloy steel and stainless steel. Diamond cutting discs are a type of cutting tool used for processing hard and brittle materials such as stone, concrete, precast slabs, old and new roads, and ceramics. Diamond cutting discs mainly consist of two parts.
10/18
For example: The balance problem caused by the manufacturing of grinding wheels that do not meet standards. An unbalanced grinding wheel will produce vibrations when operating at high speeds, which affects the grinding quality and subsequently the quality of the castings. If the size standards of the grinding wheels are not strict, it can lead to matching issues between the chuck and the grinding wheel, resulting in waste of equipment and materials, and it does not meet requirements, which can easily cause personal accidents. Therefore, choosing a suitable grinding wheel product can not only improve the quality of castings but also reduce waste, lower costs, and avoid certain accidents.